The Evolution of Radiology: From X-rays to Digital Imaging

The Birth of Radiology: Understanding X-rays
Radiology began in 1895 when Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen discovered X-rays. This groundbreaking finding allowed doctors to see inside the human body without invasive procedures. Imagine being able to look through a wall to see what's happening behind it; that's what X-rays did for medicine. Doctors quickly recognized the potential of this technology, and it transformed diagnostic practices almost overnight.
The greatest advances in medical imaging have made it possible to see inside the body without ever having to make an incision.
Initially, X-ray technology was rudimentary, with images being grainy and difficult to interpret. However, the ability to diagnose fractures and other internal issues without surgery was revolutionary. It was like discovering a new lens to view human anatomy, making it easier to understand complex medical conditions. Over time, the equipment evolved, becoming more user-friendly and effective.
As the use of X-rays grew, so did concerns about radiation exposure. Safety measures began to be implemented to protect both patients and medical staff. This marked the beginning of a journey towards safer imaging practices, which would only continue to evolve as technology advanced.
Advancements in Imaging: The Role of CT Scans
In the 1970s, the introduction of computed tomography (CT) scans marked a significant leap forward in radiology. Unlike traditional X-rays, CT scans use computer processing to create detailed cross-sectional images of the body. Think of it as slicing a loaf of bread to see the inside; this technology provided a clearer view of organs and tissues.
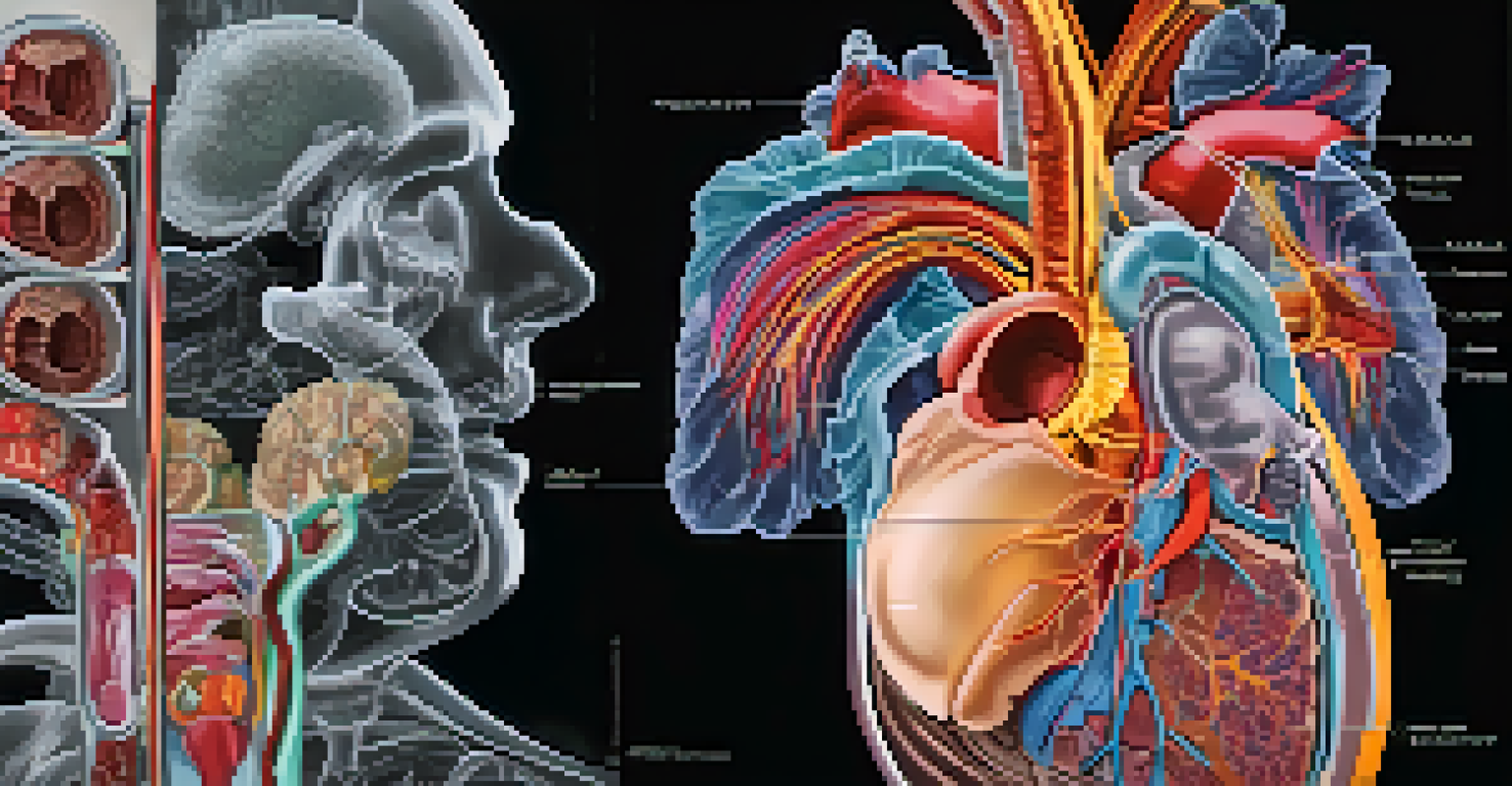
CT scans helped in diagnosing a myriad of conditions, from tumors to internal injuries, with much greater accuracy. This advancement was particularly beneficial in emergency medicine, where time is of the essence. With CT technology, doctors could quickly assess a patient's condition and make informed decisions.
Radiology's Evolution Through Technology
From the discovery of X-rays to advanced imaging techniques like MRI and CT scans, radiology has significantly transformed diagnostic medicine.
However, the increased detail came with a trade-off: higher doses of radiation. This raised new questions about patient safety, leading to ongoing research aimed at optimizing scan protocols and minimizing exposure. The balance between image quality and safety became a central theme in the evolution of radiology.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging: A New Dimension
The 1980s ushered in another revolutionary imaging technique: magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). Unlike X-rays and CT scans, MRI uses powerful magnets and radio waves to create detailed images of soft tissues. This made it particularly useful for imaging the brain, muscles, and ligaments, areas where traditional X-rays fell short.
Radiology is the key to understanding the human body and diagnosing conditions that would otherwise remain hidden.
MRIs allowed for a level of detail that transformed diagnostic capabilities, giving doctors new insights into conditions such as strokes, tumors, and joint injuries. Picture it like having a high-definition camera instead of a standard one; the clarity and depth provided invaluable information for treatment planning.
Despite its advantages, MRI technology also posed challenges, such as longer scan times and the need for patients to remain still. Additionally, the claustrophobic nature of MRI machines made it difficult for some patients. Nonetheless, ongoing advancements have improved patient comfort and reduced scan times, making MRIs a staple in modern medicine.
Ultrasound Imaging: Safe and Versatile
Ultrasound imaging made its mark in the mid-20th century and has since become one of the safest imaging methods available. It uses sound waves to produce images of organs and structures inside the body, making it particularly valuable for monitoring pregnancies. Think of it as using sonar to navigate through the body, providing a real-time view without any radiation exposure.
One of the key benefits of ultrasound is its versatility. It can be used for various medical applications, from examining the heart to guiding biopsies. This adaptability has made it a favorite among healthcare providers, especially in obstetrics and emergency medicine.
Importance of Patient Safety
As imaging technology advanced, so did concerns about radiation exposure, leading to improved safety measures for patients and healthcare providers.
Moreover, the technology continues to evolve, with advancements like 3D and 4D ultrasound providing even more detailed images. These innovations have not only enhanced diagnostic capabilities but also improved the overall patient experience, allowing families to bond with unborn children in a unique way.
Digital Imaging: The Dawn of a New Era
The late 20th century saw the transition from traditional film-based imaging to digital imaging, revolutionizing the field of radiology. Digital images can be easily stored, shared, and analyzed, streamlining the workflow for healthcare providers. Imagine going from physical books to e-books; digital imaging made accessing and interpreting medical images faster and more efficient.
Digital radiography offers numerous advantages, including enhanced image quality and the ability to manipulate images for better clarity. This technology also reduces the need for chemical processing, making it more environmentally friendly. As a result, healthcare facilities began adopting digital systems to improve diagnostic accuracy and patient care.
The integration of digital imaging with advanced software has paved the way for artificial intelligence (AI) applications in radiology. These tools can assist radiologists in detecting abnormalities with greater accuracy, further enhancing the efficiency of the diagnostic process. This synergy between technology and medicine exemplifies the exciting future of radiology.
Telemedicine and Remote Radiology: Expanding Access
The rise of telemedicine has dramatically changed how radiology is practiced, especially in remote or underserved areas. Radiologists can now interpret images from anywhere in the world, enabling timely diagnoses and consultations. Imagine a skilled doctor in a city providing expert analysis to a clinic in a rural area; this connectivity is revolutionizing patient care.
Remote radiology services have become increasingly critical, particularly during emergencies or public health crises. This accessibility ensures that patients receive prompt evaluations, regardless of their location. It also alleviates the burden on local healthcare facilities, allowing them to focus on immediate care needs.
Future Innovations in Radiology
The future of radiology looks promising with innovations like AI and molecular imaging, which aim to enhance diagnostic accuracy and personalize patient care.
However, this shift also presents challenges, such as ensuring the security and privacy of patient data. As the world becomes more connected, the importance of robust cybersecurity measures in telemedicine cannot be overstated. Balancing accessibility with security will be key as radiology continues to evolve in this digital age.
The Future of Radiology: Innovations on the Horizon
As we look to the future, the field of radiology is poised for even more groundbreaking advancements. Innovations such as 3D imaging, molecular imaging, and AI-driven diagnostics promise to enhance our understanding of complex medical conditions. These technologies could provide deeper insights than ever before, allowing for more personalized treatment plans.
Moreover, the integration of patient data with imaging results is becoming increasingly important. By combining imaging with genetic and clinical information, healthcare providers can develop tailored strategies to address individual health needs. Picture it as assembling a puzzle; every piece of information contributes to a clearer picture of the patient's health.
The ongoing collaboration between technology and medicine will shape the future of radiology. As we embrace these advancements, the potential to improve patient outcomes and streamline healthcare processes is immense. The journey from X-rays to digital imaging is just the beginning of a new era in medical diagnostics.