Integrating Simulation into Medical School Curricula
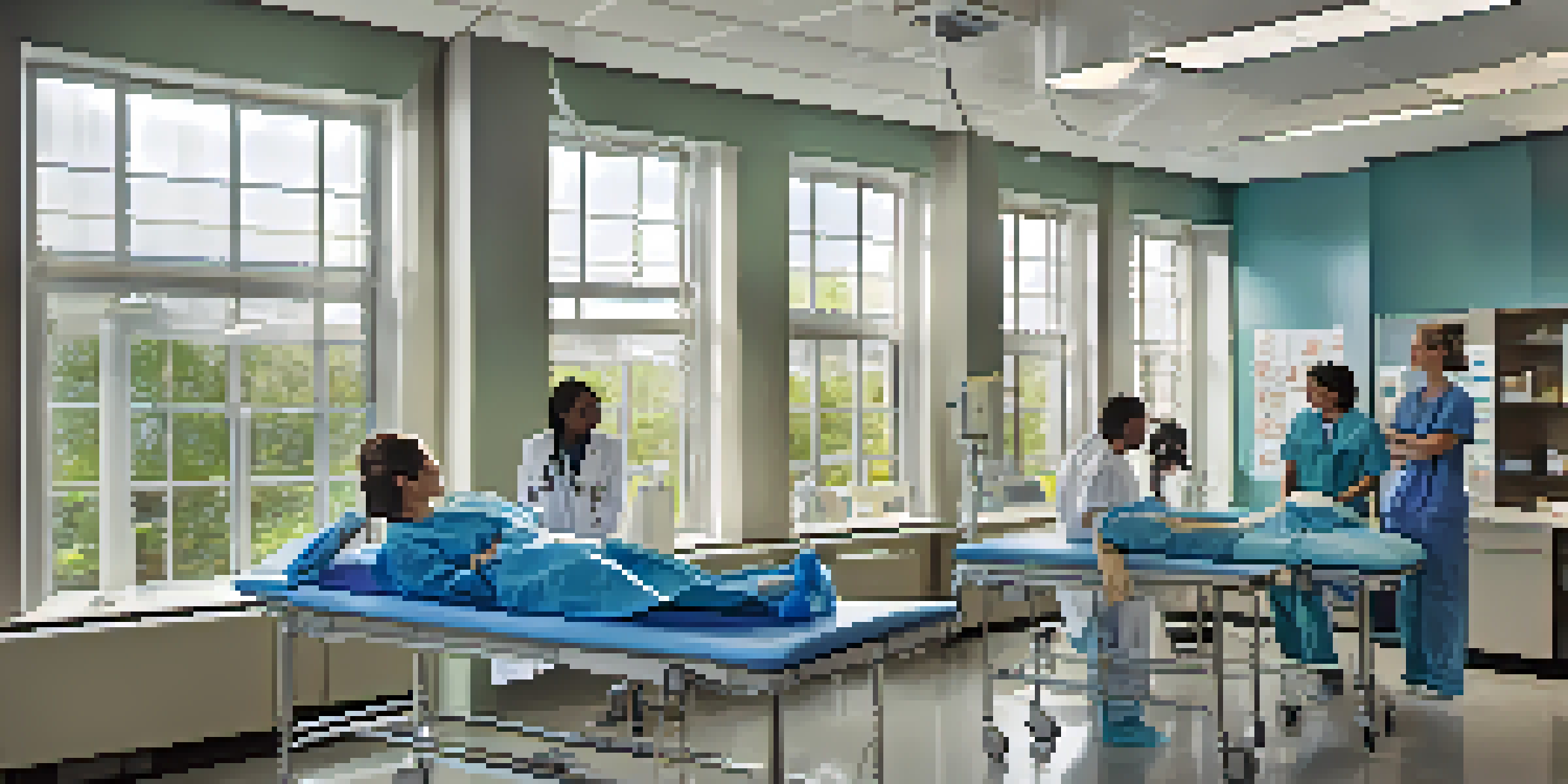
Understanding the Role of Simulation in Medical Education
Simulation in medical education refers to the use of realistic scenarios that mimic clinical situations. It enables students to practice skills in a safe environment without risking patient safety. By engaging in simulations, students can explore critical thinking and decision-making processes essential for real-world practice.
The greatest danger in times of turbulence is not the turbulence; it is to act with yesterday's logic.
For instance, a student might use a high-fidelity mannequin to practice responding to a cardiac arrest scenario. This hands-on experience helps bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical application, allowing students to learn from their mistakes without consequences.
Furthermore, simulation fosters a deeper understanding of complex medical concepts. It encourages active learning and promotes retention, making it a vital component of modern medical curricula.
Benefits of Simulation Training for Medical Students
The primary benefit of simulation training is the opportunity for repetitive practice. Medical students can rehearse procedures multiple times, gaining confidence with each attempt. This practice is invaluable, particularly for intricate techniques that require precision and skill.

Additionally, simulations can promote teamwork and communication among students. In many scenarios, students must collaborate, mirroring the dynamics of a real healthcare team. This collaboration not only enhances interpersonal skills but also prepares students for the collaborative nature of medical practice.
Simulation Enhances Medical Skills
Simulation in medical education allows students to practice clinical scenarios in a safe environment, bridging the gap between theory and practical application.
Moreover, simulation can be tailored to address specific learning needs or gaps in knowledge. Whether it's mastering a surgical technique or improving diagnostic skills, simulations can be modified to meet individual student requirements.
Types of Simulation Used in Medical Education
Medical schools utilize various types of simulation, including high-fidelity mannequins, virtual reality, and standardized patient encounters. High-fidelity mannequins can mimic real-life physiological responses, providing students with a lifelike experience. This technology allows for a detailed exploration of patient care.
Education is not the filling of a pail, but the lighting of a fire.
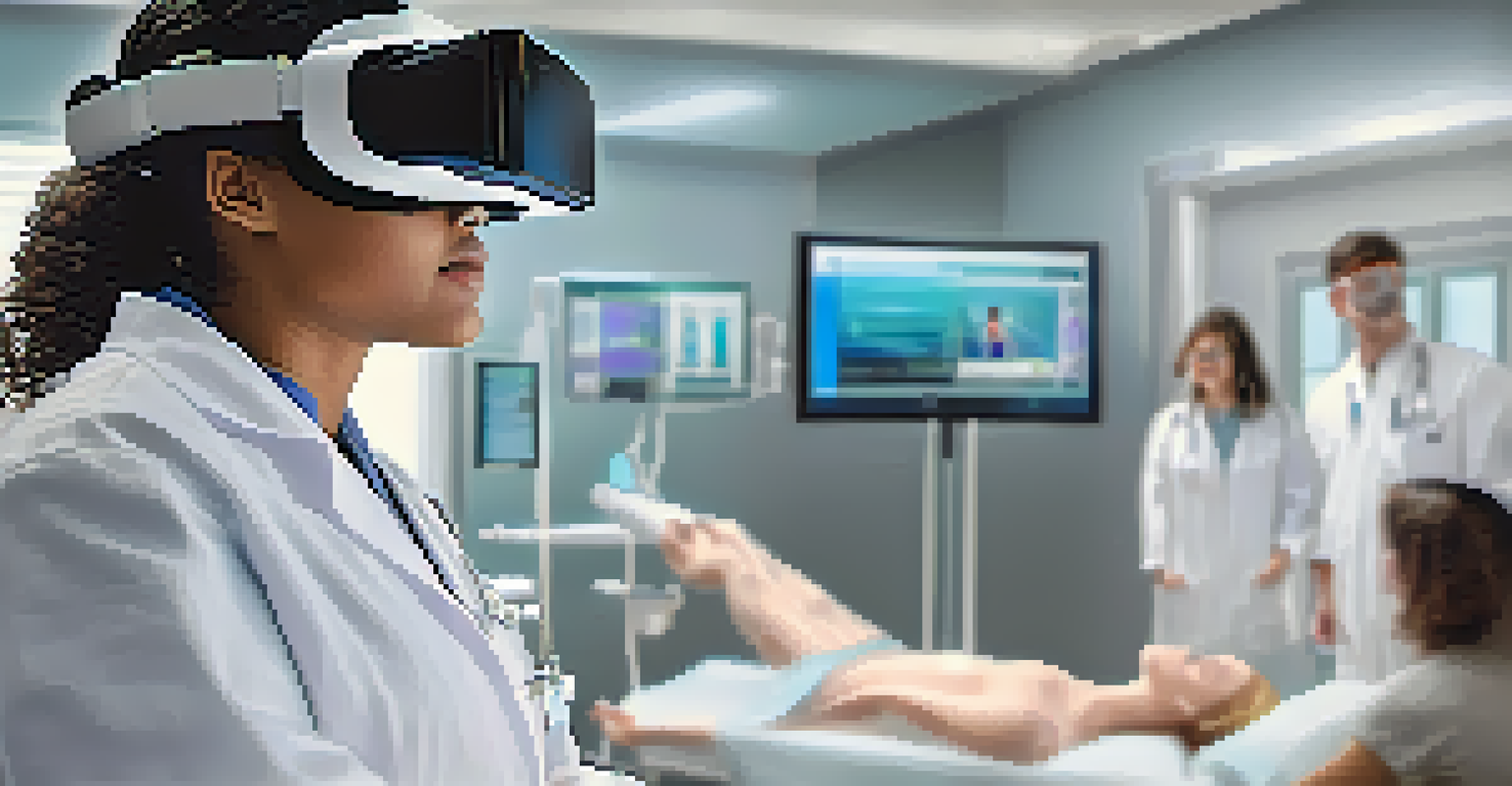
On the other hand, virtual reality simulations offer an immersive experience where students can engage in complex scenarios from anywhere. This flexibility can enhance accessibility to training resources, especially for remote learners.
Standardized patient encounters involve actors trained to present specific medical conditions, allowing students to practice their clinical skills in a controlled environment. This method helps develop communication skills and bedside manner, which are crucial in patient interactions.
Challenges in Implementing Simulation Programs
While the benefits of simulation are clear, there are challenges in implementing these programs in medical schools. One major hurdle is the cost associated with high-fidelity simulators and the maintenance of equipment. Budget constraints can limit the availability of these resources, affecting the quality of training.
Additionally, faculty may require additional training to effectively integrate simulation into their teaching methods. This transition may necessitate time and resources that some institutions may struggle to allocate.
Teamwork is Key in Simulations
Simulation training promotes collaboration among students, preparing them for the teamwork essential in real healthcare settings.
Lastly, ensuring that simulations are relevant and aligned with current medical practices is essential. As medical knowledge and technology evolve, curricula must be continuously updated to reflect these changes, which can be a daunting task for educators.
Evaluating the Effectiveness of Simulation-Based Learning
To ensure that simulation-based learning is effective, institutions must implement robust evaluation methods. Feedback from students and faculty can provide insights into the strengths and weaknesses of the program. This feedback loop is crucial for making necessary adjustments and improvements.
Quantitative measures, such as assessments and performance metrics, can help gauge student progress and competencies. By analyzing these metrics, educators can identify trends and areas that require additional focus or resources.
Moreover, qualitative assessments, such as student reflections and peer evaluations, can provide deeper insights into the learning experience. This combination of evaluation methods creates a comprehensive understanding of the impact of simulation on student learning outcomes.
Future Trends in Medical Simulation Education
The future of medical simulation education looks promising, with advancements in technology paving the way for more immersive experiences. Innovations such as augmented reality (AR) and artificial intelligence (AI) are beginning to play a role in enhancing simulation training. These technologies can create more personalized learning experiences that adapt to individual student needs.
Additionally, the integration of telemedicine training into simulation programs is becoming increasingly important. As telehealth continues to grow, future physicians must be equipped with the skills to navigate virtual patient interactions effectively.
Future Trends in Medical Education
Advancements like augmented reality and telemedicine training are shaping the future of medical simulation, creating more personalized learning experiences.
Furthermore, collaboration among institutions to share best practices and resources can lead to a more standardized approach to simulation training. This collective effort can enhance the overall quality of medical education across the board.
Creating an Inclusive Learning Environment with Simulation
Integrating simulation into medical education can also foster inclusivity by accommodating diverse learning styles. For instance, visual learners may benefit from watching procedures on simulators, while kinesthetic learners thrive through hands-on practice. This adaptability ensures that all students can engage with the material in a way that resonates with them.
Moreover, simulations can be designed to reflect various patient demographics and clinical scenarios, promoting cultural competence among future physicians. Exposure to a range of cases helps students understand and appreciate the diverse backgrounds of their future patients.
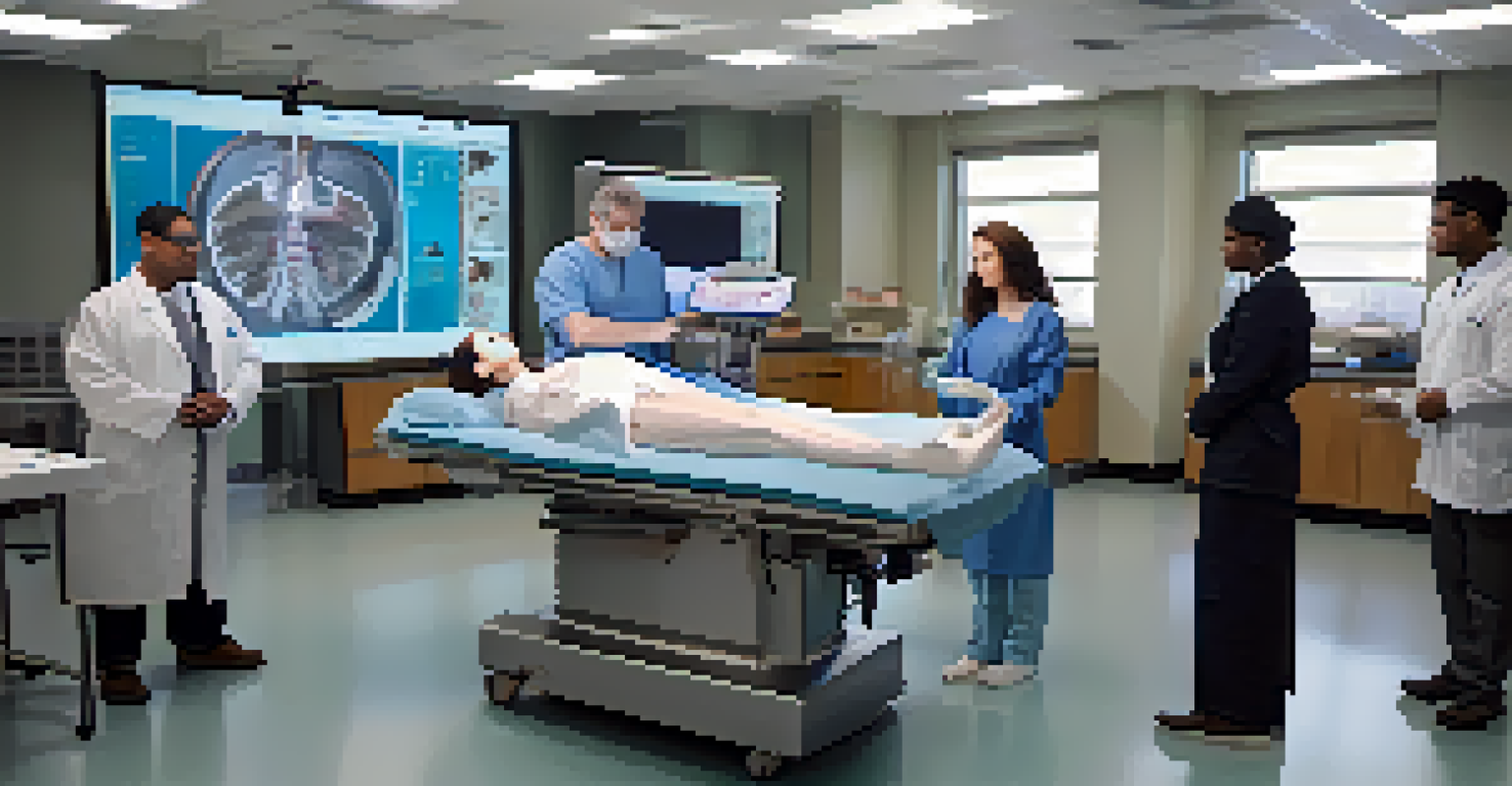

Additionally, creating a supportive environment where students can learn from mistakes without fear encourages psychological safety. This approach promotes resilience and adaptability, qualities that are essential for success in the medical field.