Transdermal Drug Delivery: Innovations and Challenges
Understanding Transdermal Drug Delivery Systems
Transdermal drug delivery systems (TDDS) offer a unique way to administer medication through the skin. Unlike traditional methods like pills or injections, TDDS can provide a steady release of drugs over time. This approach not only enhances patient compliance but also minimizes the fluctuations in drug levels in the bloodstream. By bypassing the digestive system, transdermal systems can also reduce the risk of gastrointestinal side effects.
The skin is a barrier, but with the right innovations, it can also be a pathway for healing.
One of the key components of TDDS is the transdermal patch, which adheres to the skin and releases medication gradually. These patches can be used for various medications, including pain relief and hormone replacement therapies. The convenience of a patch means that patients can go about their daily activities without the need for frequent dosing. This makes TDDS particularly appealing for chronic conditions where ongoing treatment is necessary.
However, understanding how drugs penetrate the skin is crucial for effective transdermal delivery. The skin acts as a barrier, and not all drugs can easily pass through. Researchers are continuously studying the properties of the skin and how to enhance drug permeation, which leads us to the innovations in this field.
Recent Innovations in Transdermal Drug Delivery
Innovations in transdermal drug delivery are making headlines, especially with the advent of microneedle technologies. These tiny needles create micro-channels in the skin, allowing drugs to be delivered more effectively without causing significant pain. For example, microneedle patches have been developed for vaccines, enabling a pain-free alternative to traditional injections.

Another exciting development is the use of nanotechnology to enhance drug formulations for transdermal applications. Nanoparticles can improve the solubility and stability of medications, making it easier for them to penetrate the skin barrier. This not only improves the efficacy of the drugs but also allows for lower doses, reducing potential side effects.
Benefits of Transdermal Delivery
Transdermal drug delivery systems provide a steady release of medication, enhancing patient compliance and minimizing side effects.
Smart transdermal systems are also gaining traction, integrating sensors that monitor drug levels and patient adherence. These systems can adjust the drug release based on real-time feedback, ensuring that patients receive the right dose at the right time. Such innovations hold great promise for personalized medicine, making treatment more effective and tailored to individual needs.
Challenges Facing Transdermal Drug Delivery
Despite the advancements, transdermal drug delivery faces several challenges that researchers are actively trying to overcome. One major issue is the variability in skin permeability among individuals, which can affect drug absorption rates. Factors such as age, skin condition, and hydration levels can lead to inconsistent therapeutic outcomes.
Transdermal delivery systems represent a leap forward in how we think about medication, making it more accessible and less intrusive for patients.
Additionally, not all drugs are suitable for transdermal delivery due to their molecular size and properties. Larger molecules, like proteins and peptides, often struggle to penetrate the skin effectively. This limitation restricts the range of medications that can be delivered via this method, leaving a gap in treatment options for certain conditions.
Moreover, the stability of drugs in transdermal formulations can be problematic. Some medications may degrade when exposed to light or air, necessitating the development of specialized packaging or formulations. Addressing these challenges is crucial for the future success of transdermal drug delivery systems.
Regulatory Considerations for TDDS
The regulatory landscape for transdermal drug delivery systems is essential to ensure patient safety and efficacy. Regulatory agencies, like the FDA, have specific guidelines for the approval of transdermal products. These regulations focus on aspects such as drug formulation, delivery method, and clinical efficacy.
Manufacturers must conduct thorough clinical trials to demonstrate the safety and effectiveness of their transdermal products. This process can be lengthy and costly but is crucial for gaining consumer trust. Moreover, post-market surveillance is also necessary to monitor long-term effects and any potential adverse reactions after the product is launched.
Innovations in Drug Delivery
Recent advancements like microneedle technology and smart patches are improving the efficacy and personalization of transdermal therapies.
Navigating the regulatory framework can be challenging, especially with the rapid pace of innovation in this field. As new technologies emerge, regulatory agencies must adapt their guidelines to effectively evaluate these advancements while ensuring that public safety remains a priority.
Patient Acceptance and Adherence to TDDS
Patient acceptance is a vital aspect of the success of transdermal drug delivery systems. While many patients appreciate the convenience of patches, some may be hesitant due to concerns about skin irritation or the visible presence of a patch. Education and awareness can play a key role in alleviating these fears and improving acceptance rates.
Adherence to medication regimens is another challenge that TDDS aims to address. By providing a continuous drug release mechanism, these systems can enhance adherence compared to traditional dosing methods. Patients are less likely to forget doses when they only need to apply a patch every few days or weeks.
Ultimately, the success of transdermal drug delivery systems hinges on understanding patient preferences and addressing their concerns. Engaging with patients to gather feedback can lead to improvements in both product design and user experience, fostering a more positive reception in the market.
Future Prospects of Transdermal Drug Delivery
The future of transdermal drug delivery looks promising as researchers continue to explore new technologies and methodologies. One exciting area of investigation is the use of bioresponsive patches that can change their drug release profiles in response to physiological signals. This could revolutionize how we approach medication for conditions like diabetes or hypertension.
Moreover, the integration of digital health solutions with transdermal systems is on the rise. Imagine a patch that not only delivers medication but also tracks vital signs and provides feedback to healthcare providers. This level of connectivity could enhance patient care and enable more personalized treatment plans.
Challenges in TDDS Adoption
Variability in skin permeability and regulatory hurdles pose significant challenges for the widespread acceptance of transdermal drug delivery systems.
As the need for innovative drug delivery methods grows, transdermal systems are likely to become an integral part of modern medicine. With ongoing research and collaboration between scientists, healthcare professionals, and regulatory bodies, the potential for transdermal drug delivery is boundless.
Conclusion: Balancing Innovations and Challenges
In conclusion, transdermal drug delivery systems represent a significant advancement in medication administration. While innovations like microneedles and smart patches are paving the way for more effective treatments, challenges such as skin variability and regulatory hurdles remain. The key to success lies in balancing these innovations with practical solutions to overcome existing obstacles.
As the field progresses, ongoing communication between researchers, manufacturers, and patients will be critical. Involving patients in the development process can lead to products that not only meet medical needs but also align with their preferences and lifestyles. This collaborative approach can ultimately enhance the effectiveness and acceptance of transdermal drug delivery systems.
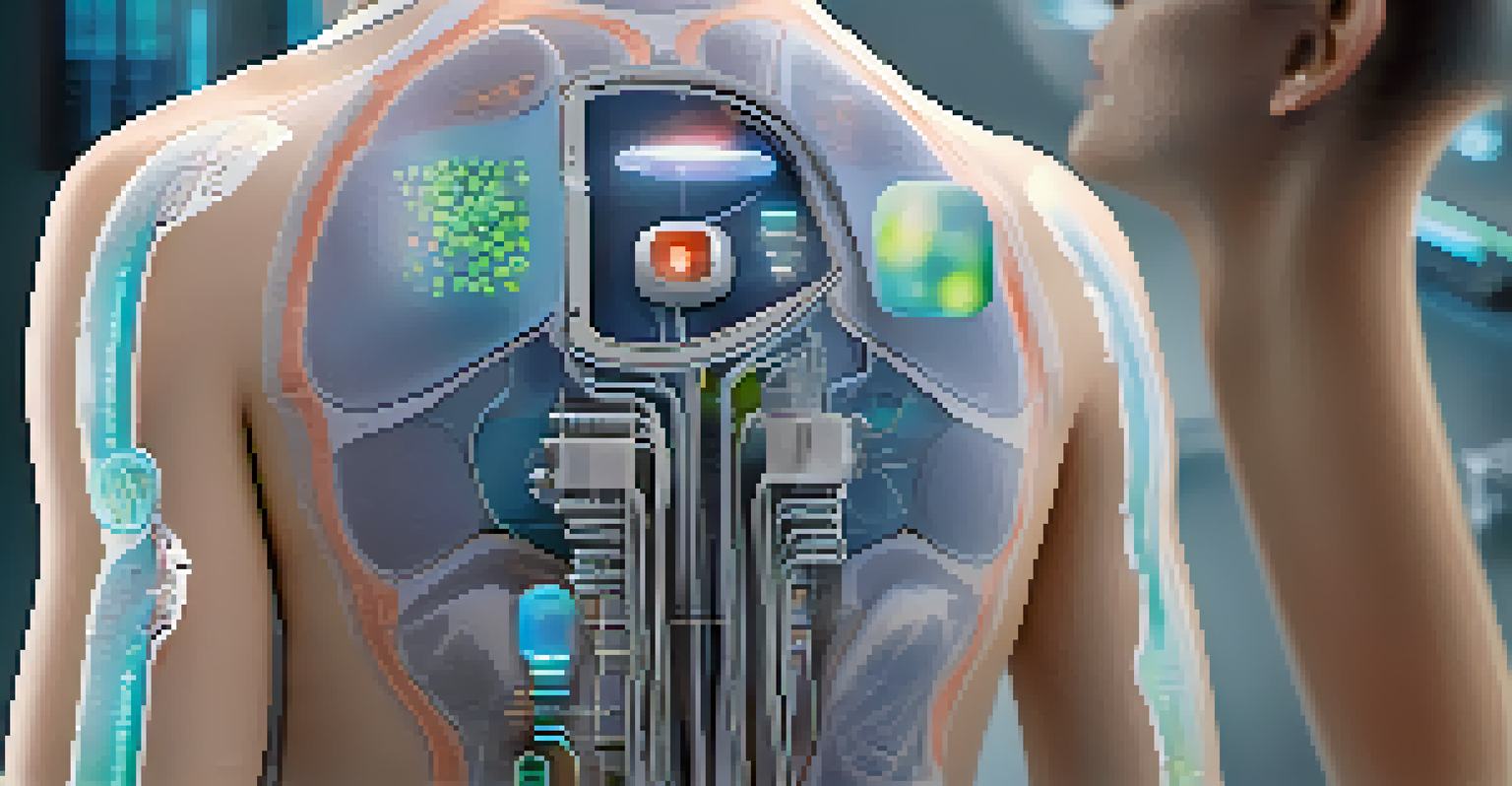
Ultimately, the landscape of transdermal drug delivery is ever-evolving. By embracing innovations while addressing challenges, we can look forward to a future where these systems play a crucial role in improving patient care and outcomes.