Innovations in Medical Simulation for Healthcare Education
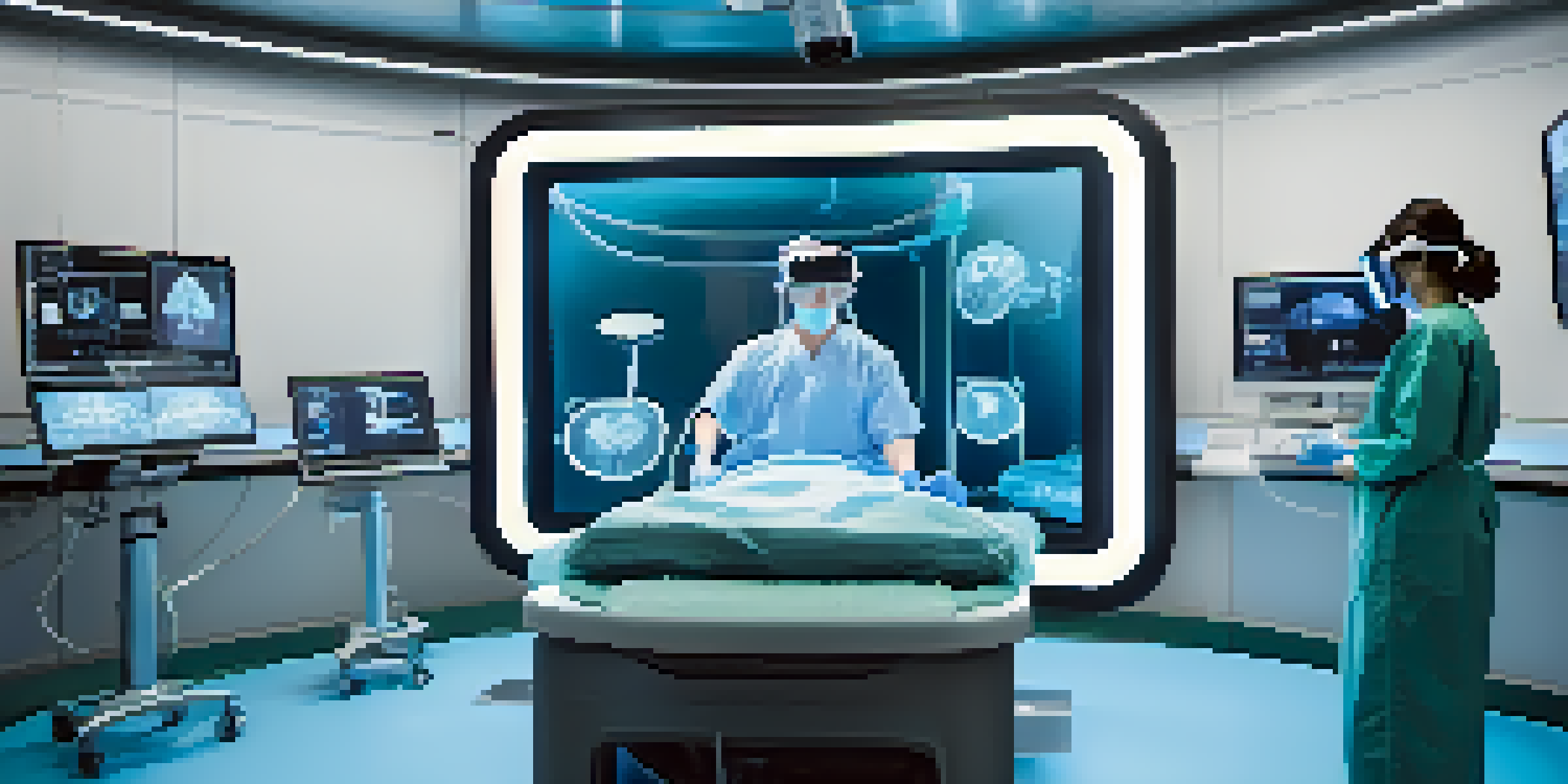
Understanding Medical Simulation in Healthcare Education
Medical simulation refers to the use of advanced technologies to replicate real-life clinical scenarios for educational purposes. This innovative approach helps healthcare professionals practice and hone their skills in a controlled environment. From virtual patients to lifelike mannequins, these tools bridge the gap between theory and practice, making learning more effective.
Simulation-based education is the closest we can get to real-life experience without putting patients at risk.
In traditional education, students often learn through lectures and textbooks, which can leave gaps in practical experience. Medical simulation fills these gaps by allowing learners to engage in hands-on practice without the risk of harming actual patients. This experiential learning is crucial for building the confidence and competence necessary in high-stakes healthcare settings.
Moreover, medical simulation is not just limited to students; it’s also beneficial for experienced professionals. Regular training on new techniques and technologies ensures that healthcare providers stay updated and can provide the best care possible. This continuous learning culture is essential in a field that evolves rapidly.
Advancements in Virtual Reality for Medical Training
Virtual reality (VR) has emerged as a game-changer in medical simulation, offering immersive experiences that replicate real-world medical procedures. With VR, healthcare students can step into a virtual operating room, practice surgeries, or manage emergency situations without any real-life consequences. This level of engagement can significantly enhance retention and understanding of complex medical concepts.

One of the standout features of VR is its ability to provide immediate feedback. As learners navigate through procedures, they can receive real-time assessments of their performance, allowing them to identify areas for improvement. This instant feedback loop is invaluable, as it helps students refine their skills before ever interacting with real patients.
Simulation Enhances Practical Skills
Medical simulation allows healthcare professionals to practice real-life scenarios in a safe environment, bridging the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical skills.
Additionally, VR can be accessed remotely, making it an excellent option for institutions with limited resources. By integrating VR into their curriculum, educational institutions can offer high-quality training experiences to a broader range of students, regardless of geographical barriers. This democratization of education is a significant step forward in healthcare training.
The Role of Augmented Reality in Medical Education
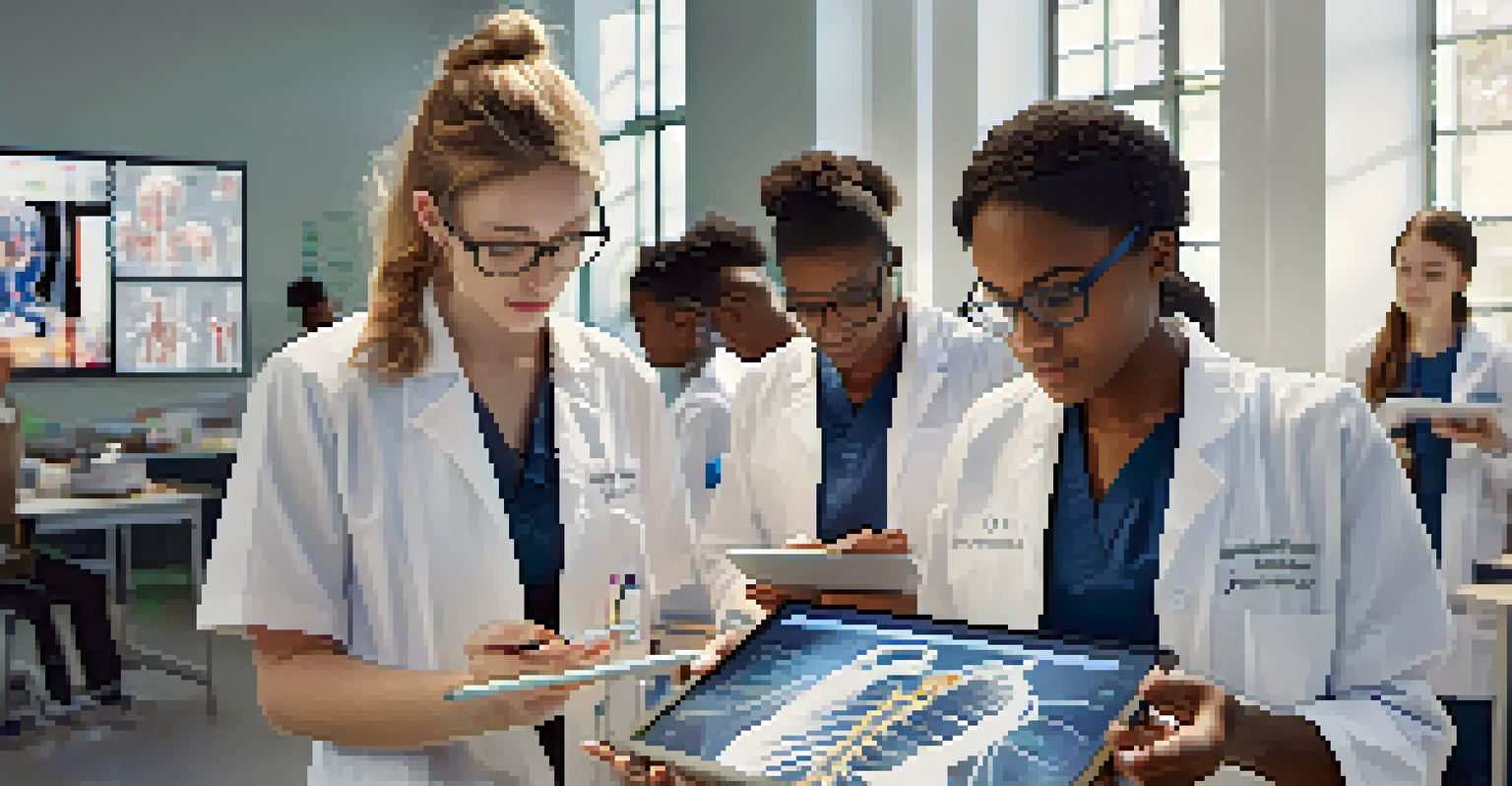
Augmented reality (AR) overlays digital information onto the real world, providing a unique approach to medical education. For instance, during anatomy lessons, students can use AR to visualize organs and systems in 3D, making complex structures easier to understand. This interactive learning method enhances engagement and fosters a deeper appreciation for human anatomy.
The use of virtual reality in medical training is revolutionizing the way we prepare future healthcare professionals.
AR also allows for real-time collaboration in training scenarios. Multiple students can interact with the same augmented environment, facilitating teamwork and communication skills essential for healthcare professionals. This collaborative aspect mirrors real-life medical situations where teamwork is vital for effective patient care.
Furthermore, AR can be particularly useful in continuing education for healthcare providers. By using AR applications, professionals can refresh their skills and knowledge while keeping up with the latest advancements in medical technology. This ongoing education is crucial in maintaining high standards of patient care.
Simulation-Based Assessment for Healthcare Professionals
One of the most significant benefits of medical simulation is its ability to serve as an assessment tool. Simulation-based assessments provide a comprehensive evaluation of a healthcare professional's skills in a realistic setting. This method goes beyond traditional testing, allowing evaluators to observe how individuals handle pressure and make critical decisions.
For example, high-fidelity simulations can replicate emergency scenarios where quick thinking is essential. Evaluators can assess not only clinical skills but also communication and teamwork abilities in these high-stress situations. This holistic approach to assessment ensures that healthcare providers are well-prepared for real-life challenges.
VR and AR Transform Learning
Advancements in virtual and augmented reality create immersive training experiences that improve retention and understanding of complex medical procedures.
Moreover, simulation-based assessments can highlight areas where additional training is needed. By identifying specific weaknesses, institutions can tailor their educational programs to address these gaps, ultimately improving the overall quality of healthcare education. This data-driven approach fosters a culture of continuous improvement.
Ethical Considerations in Medical Simulation
As with any innovative approach, ethical considerations in medical simulation are paramount. One of the primary concerns is ensuring that simulations do not inadvertently mislead students about real-life practices. It’s crucial that learners understand the limitations of simulations and the complexities involved in actual patient care.
Additionally, the use of realistic mannequins and virtual patients raises questions about consent and emotional impact. Educators must be sensitive to the psychological effects of training on students, particularly when scenarios involve severe medical conditions or ethical dilemmas. Providing appropriate support and debriefing sessions can help mitigate these concerns.
Lastly, accessibility is an ethical issue that must be addressed. Not all institutions have the resources to implement high-tech simulations, which could create disparities in education. It is essential for educational leaders to advocate for equitable access to simulation technologies, ensuring that all healthcare professionals receive the training they need.
Integrating Simulation into Traditional Curriculum
Integrating medical simulation into traditional healthcare education requires careful planning and collaboration among educators. By incorporating simulation exercises into existing curricula, educators can enhance learning outcomes and student engagement. This integration allows students to build on theoretical knowledge with practical, hands-on experience.
One effective strategy is to use simulations as a capstone project, where students apply their knowledge to solve complex clinical problems. This approach encourages critical thinking and reinforces the importance of teamwork and communication skills. It also prepares students for the realities they will face in their careers.
Ethics and Accessibility Matter
Ethical considerations, including consent and equitable access to simulation technologies, are crucial to ensure that all healthcare professionals receive quality training.
Moreover, faculty training is essential to ensure that educators feel confident in using simulation technologies. Providing professional development opportunities can help instructors become proficient in designing and facilitating simulation experiences, ultimately benefiting students. This investment in faculty leads to a more robust educational environment.
Future Trends in Medical Simulation Technology
The future of medical simulation is bright, with ongoing advancements poised to further transform healthcare education. Innovations such as artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are beginning to play a role in creating more adaptive and personalized training experiences. These technologies can analyze a learner's performance and adjust scenarios to better suit their individual needs.
Moreover, the integration of wearable technology is on the horizon, allowing for real-time monitoring of physiological responses during simulations. This data can provide valuable insights into stress management and decision-making under pressure, enhancing the overall learning experience. Imagine learners being able to see their heart rates and other metrics while practicing critical skills!
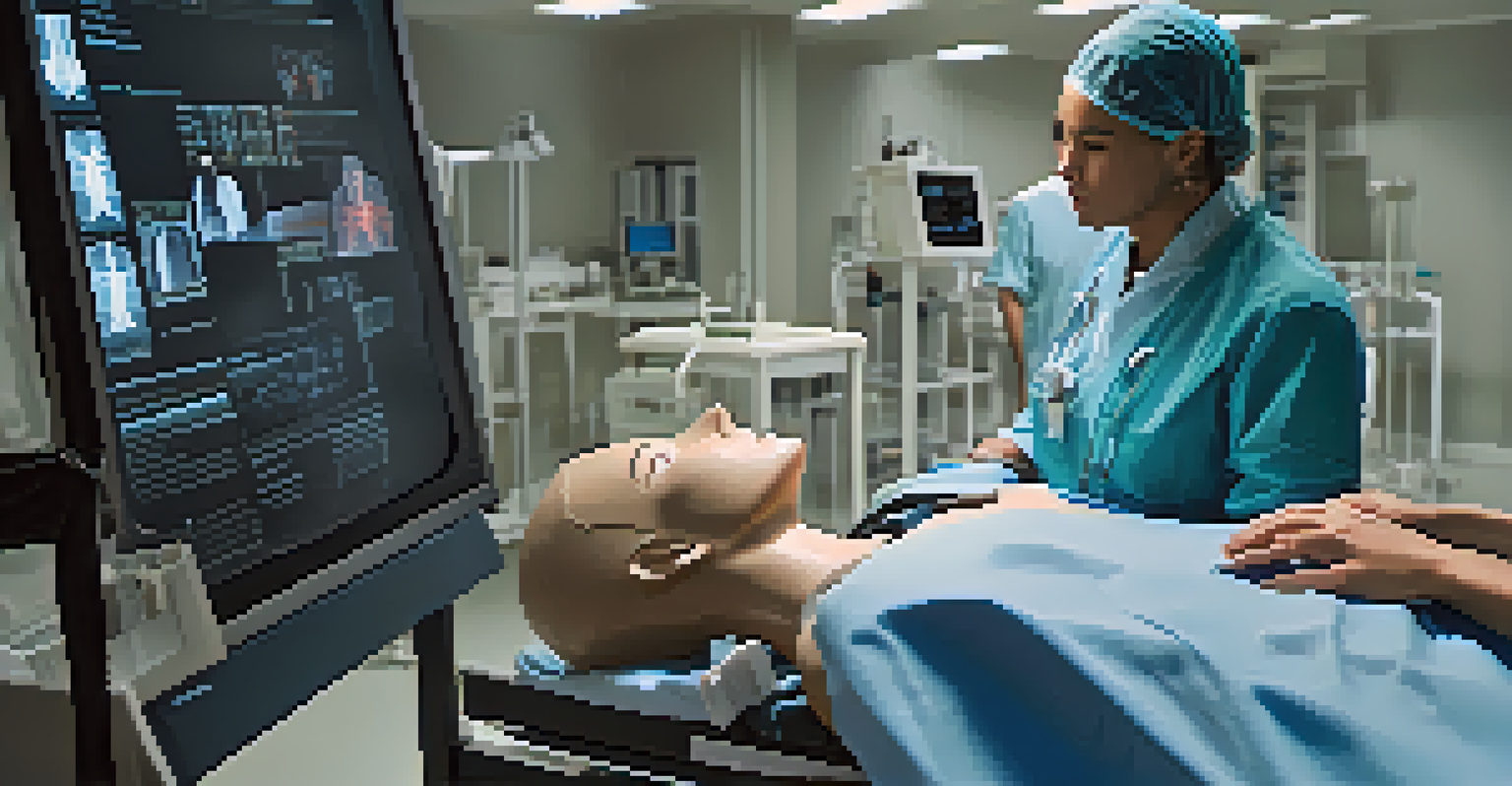
Finally, we can expect an increase in collaboration between healthcare institutions and tech companies. As the demand for innovative training solutions grows, partnerships will likely lead to the development of even more advanced simulation tools. This collaborative approach ensures that healthcare education remains at the forefront of technological advancement, ultimately improving patient care.